
- #Applocker group policy how to#
- #Applocker group policy install#
- #Applocker group policy windows 10#
- #Applocker group policy pro#
- #Applocker group policy software#
#Applocker group policy windows 10#
Support tip - Deploy OMA-URIs to target a CSP through Intune, and a comparison to on-premisesīase on Microsoft AppLocker CSP supported by almost all Windows 10 Versions as you can see here.įor more details you can read in Configuration service provider reference If you are interesting to deep into CSP, OMA-URI and Applocker CSP you can find more details here

When the OMA-URI reach the Device the CSP read them and configure accordingly.īelow you can see a detail image from Microsoft which represent how OMA-URI and CSP works to apply a configuration in the device Applocker CSP in the Intune use the OMA-URI to represent the Applocker Policyįor example in Intune when you create the Configuration Profile with the Applocker Policy the Intune send it to the Assign devices. Microsoft use the Applocker CSP in Intune to allow or deny applications in the Devices which manage by Intune. The syntax of the OMA-URI is determine by the CSP on the client. The OMA-URI is a string that represent a custom configuration for the Windows 10 Device. In order to understand what is Applocker CSP let's first explain as simple can be what is CSP and how Intune send the Applocker Policies in the Windows Devices.ĬSP (Configuration Service Provider) is an interface that used by MDM Providers to read, set, modify, or delete configuration settings on the devices. Instead you should copy the lines from to for every Policy as you can see below.įor example here you must copy all these lines between arrows that related with the EXE Policy as you can see in Type="Exe"Ĭopy and Paste and the other lines base on the Type between to Intune use xml to identify AppLocker Policies.īut you can't copy and paste all the lines of the XML file because will not be accepted.
#Applocker group policy how to#
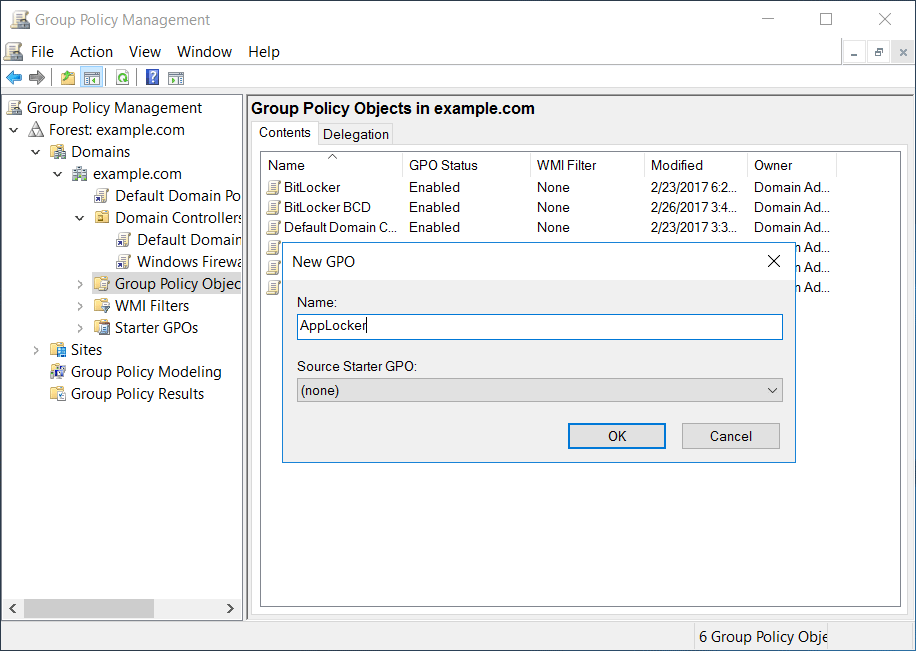
How to split the XML File to use in Intune Right click in the AppLocker and select Export Policy.Login in the Domain Controller and Edit the AppLocker Policy.How to export Applocker Rules from the GPOĪfter you have create the AppLocker Policy in your environment the next step is to export the Applocker Policy from Group Policy Management Console to get the XML file that you will need later on in Intune. However in the link you can find in which Windows Version Applocket CSP supported
#Applocker group policy install#
It's prerequisites to read the article How to install and configure Applocker to improve Application Control & Security in order to create the Applocker Policy before export in an XML file.
#Applocker group policy pro#
Remote work will be permanent and IT Pro must be ready to manage Personal or Company devices in the same Level if will be located in Office or Home.įor this reason today i will explain how can implement AppLocker in the Intune.īefore proceed in this article must be already has create and test AppLocker Policy in your environment. Intune comes to fill the gap and give a solution with the Applocker CSP which supported almost by all Windows Versions and control access in Applications for the Devices outside of your Local Network. Unfortunately Applocker it's not supported for all Windows Versions and you can't do anything for the Devices that are out of your Local Network. It's not the best solution but it's a good solution to Manage access in the Applications. You don't want to use these unless you have to.AppLocker it's a technology or whitelisting technology that allows to restricting the applications that users can execute.

Keep in mind that deny rules trump all other rules - just as is the case with most other Microsoft systems (just like with file permissions).
#Applocker group policy software#
One member should almost certainly be the SYSTEM accountĪs well as potentially the TrustedInstaller account, as it's becoming more common to see PowerShell tasks executed as part of software installers.Īlso don't forget to set up the rules in audit mode and review the success and failures to avoid accidentally and possibly seriously impacting production scenarios and users. What this leaves you with is the task of creating a new "allow" rule for which you should create a controlling security group and add as members the people/groups you wish to grant access.
If you simply add %windir%\Syswow64\WindowsPowerShell\* then that willĪlso stop the 32-bit PowerShell host from being accessible to everyone. The default rules in the above screenshot will allow everyone to run PowerShell - both 32 and 64-bit.Īs you've already pointed out, there is an exception in your implementation for the default rule that pertains to the Windows folder the excludes %windir%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\*.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
